How To Plan Your App Release With The Mobile Release Train
There are only a couple of things that can be more frustrating in agile software development than the situation when your release planning comes to a halt. One typical bottleneck is that product managers cannot work on the next release of an app that is being developed across different teams working on different aspects of the storyline.
During release planning, you soon realize that apps developed across multiple teams need an aligned approach to be released in advance. This is where the concept of the “mobile release train” comes into play. By executing this approach, your different developer teams are able to release apps to the different app stores simultaneously.
The concept is nothing new and is part of the scaled agile framework. The mobile release train describes how to deliver software in a specific way. The mobile release train can be used by small and/or big distributed departments which work on one app, but in different teams.
How To Jump On The Mobile Release Train
Let’s take a look at a mobile release train. In the picture below, you’ll see a simple example. It has a defined development phase that, in most cases, is between two to four weeks.
On a defined day and time (let’s say on a Monday at 3:00 p.m.) there is a code freeze happening. Until this time, the teams have time to review, test and merge the features to the master branch that should be part of the train. At 3:00 p.m., someone will create a release branch from the master branch, either manually or in an automated way.
This release branch will get a final integration testing phase. In this phase, all team members should check that the new features are working as expected. If there is a problem on the release branch, the bug will be fixed on the release branch and later merged back to the master branch.
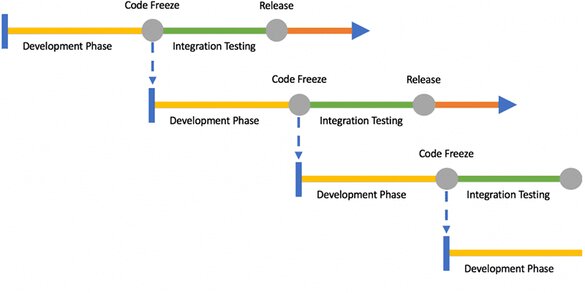
Once the code freeze happens, a new development cycle will start and all contributing teams can start a new sprint and continue with the development. The great thing about the mobile release train is that everyone knows the next planned release and can plan their work accordingly.
Who Will Be The Train Driver?
There must be one team or person handling the release. Either it’s always the same person/team or it is a shared effort among all developers. In any case, one person must be the responsible “release engineer.” This person is responsible for getting all required information for the release (e.g. release notes, new store images and so on). Furthermore, this person can organize a weekly release standup to inform the rest of the team about ongoing releases and problems that occur on the current live version.
Always Include Testing In Your Release Planning
If a team is using internal testing with colleagues, beta testing with real customers and using a staged rollout, the mobile release train can look like this:
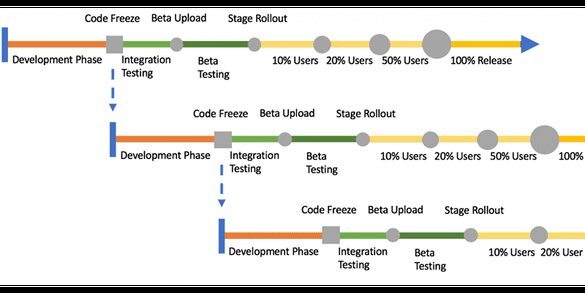
In this example, you can see a possible Android release train. The development and integration testing phases are the same as in the simple version of the train. Once the app has been tested internally or externally, the release engineer uploads the app to the beta channel. In this channel, real customers will receive an update notification on their devices for testing.
During the beta testing phase, beta testers can give direct feedback via the app store. Next to the feedback, the crashes can be monitored in tools such as TestFlight, HockeyApp or Crashlytics.
After the beta testing phase, the app will be pushed to the stage-rollout. In this stage, the release engineer can define what percentage of the users will get the update. In this case, the steps are 10%, 20% and 50% rollout. In each stage, the reviews as well as the crash tools must be monitored to check for possible problems.
If a bug becomes visible in the 20% stage, the team has the chance to react to the problem and use the mobile bug matrix to decide if the problem is worth a hot fix. If this is the case, the train should not reach the next rollout step of 50%. Instead, the problem must be fixed for 20% of the users. Once the problem is fixed and verified, the train can move on to 50%.
As in the simple version of the train, only the release engineer or the release team is taking care of the release process after the code freeze. All other teams continue with the “normal” development.
How To Establish The Mobile Release Train
Before you start to implement the mobile release train in your company, you must define the time slots for each stage. In most cases, the development phase is two to four weeks. But then you need to define how much time you want to spend doing the integration testing, beta testing and the rollout stages. Here is an example:
- 10 days of development
- Two days of integration testing
- Three days beta testing
- Two days 10% of the users
- Four days 20% of the users
- Two days 50% of the users
In total, it takes 23 days until a new app version is live for 100% of your customers. For some apps and customers that might be too fast; for others, this is way too long. Every team/company needs to define its own time slots.
If you want to establish a more advanced mobile release train for iOS, you can remove the stage-rollout and exchange it with an extended internal testing phase with your colleagues. You can distribute the app internally using tools such as TestFlight or HockeyApp. Once the internal testing phase is over, you can use the same tools to send the app to beta customers. Afterwards, you can upload the app to the App Store and release it straight to 100% of your customers.
Important Aspects To Follow While Release Planning
Establishing and using a mobile release train sounds great, but keeping the process up and running while release planning can be tough. Here are some aspects you should follow:
- One team/person must handle the release coordination and the release itself.
- Have a weekly/bi-weekly release standup to exchange between the contributing teams.
- Schedule and communicate the train departure times some weeks/months ahead.
- Only accept reviewed and tested code.
- Only accept code that has unit tests and end-to-end test automation in place (if needed).
- Don’t accept late passengers. Don’t merge code to the release branch which was still in development on code freeze day. This code hasn’t been reviewed and tested enough.
- Use stage-rollout if possible.
- Monitoring of the released app version is crucial.
